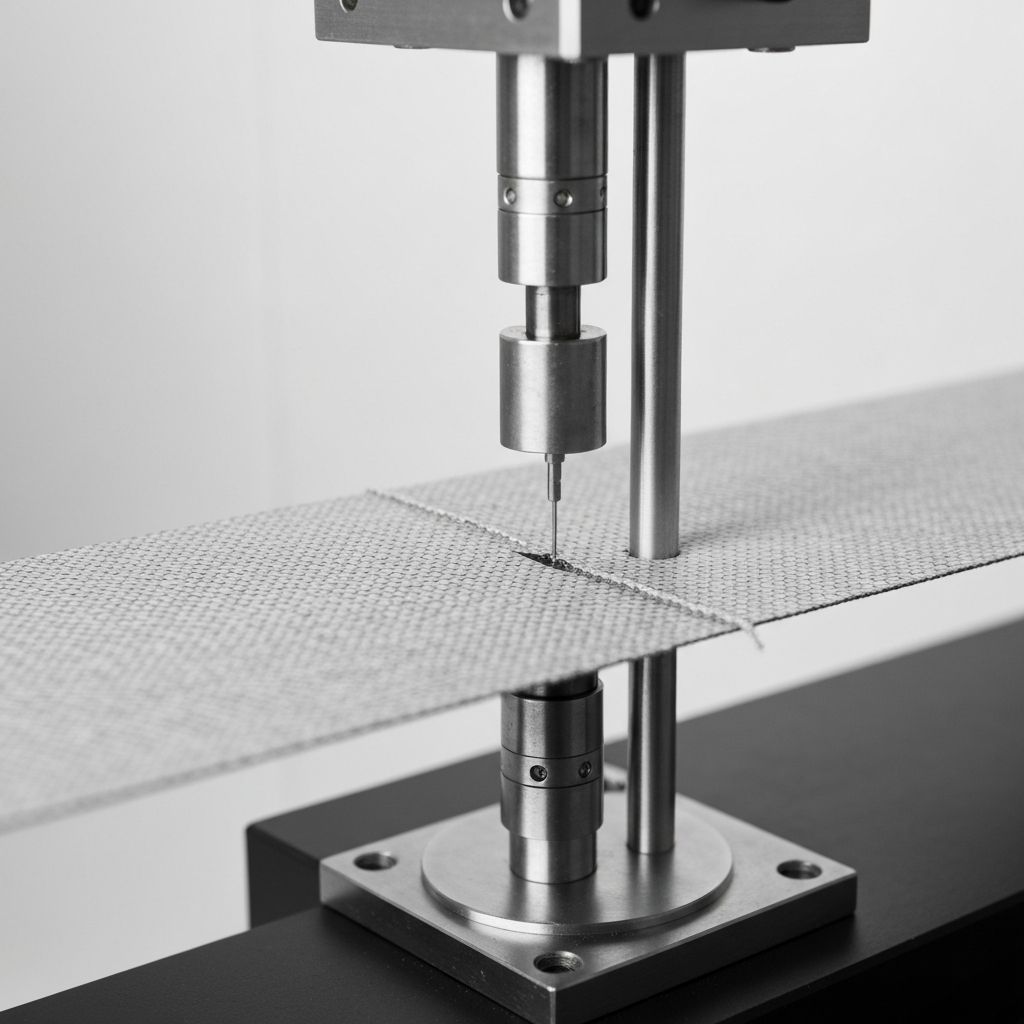
Fire safety is critical for tensile fabric structures, especially in public assembly occupancies. Building codes require fabrics meet fire performance standards for flame spread, smoke development, and ignition resistance. Fire testing verifies that fabrics have adequate fire retardant treatment and meet regulatory requirements for safe use in roofs, façades, and interior applications.
Fire Performance Requirements
European Construction Products Regulation requires Euroclass fire classification (A1-F) based on comprehensive fire testing. Class B-s1,d0 (limited combustibility, minimal smoke/droplets) is typical for fabric roofs. Most PVC-coated fabrics achieve Class B or C. National building codes specify requirements based on occupancy, location, and fire safety systems. Fabric fire performance includes ignitability, flame spread rate, heat release, smoke production, and flaming droplets.
Fire Testing Methods
European harmonized testing includes multiple methods to characterize fire behavior:
- EN 13501-1: Overall classification system combining results from multiple tests
- EN ISO 1182 (Non-combustibility): For Class A materials, most fabrics fail this test
- EN 13823 (SBI - Single Burning Item): Measures heat release, flame spread, smoke production
- EN ISO 11925-2 (Ignitability): Small flame surface ignition test
- ASTM E84 (Steiner Tunnel): North American test measuring flame spread and smoke development indices
Fire Retardant Treatments
PVC coatings inherently provide moderate fire resistance due to chlorine content which releases HCl (flame inhibitor) when heated. Additional flame retardant additives (metal hydroxides, phosphates) improve performance. PTFE and silicone coatings are inherently non-combustible. Treatments must be durable to weathering, UV exposure, and cleaning. Periodic testing verifies fire retardancy is maintained over service life.
Installation and Safety Considerations
Fire safety in tensile structures depends on fabric fire performance, structural system behavior in fire, egress design, and fire protection systems. Design considerations include separation from combustible materials, smoke venting provisions, sprinkler protection for interior applications, and emergency egress lighting. Fabric melting/shrinkage in fire can create openings for smoke venting but may also drop flaming material. Comprehensive fire safety engineering addresses all aspects.
Conclusion
Fire testing ensures tensile fabrics meet building code requirements and provide adequate fire safety. Our laboratory performs fire testing to Euroclass and ASTM standards with expert interpretation. Contact us for fabric fire resistance testing.
Related Testing Services
- Tensile Strength Testing
- Smoke Density Testing
- Heat Release Rate
- Dripping Behavior
Applicable Standards
Need This Testing Service?
Our accredited laboratories and field teams provide comprehensive testing services across Europe.
Contact Our Team