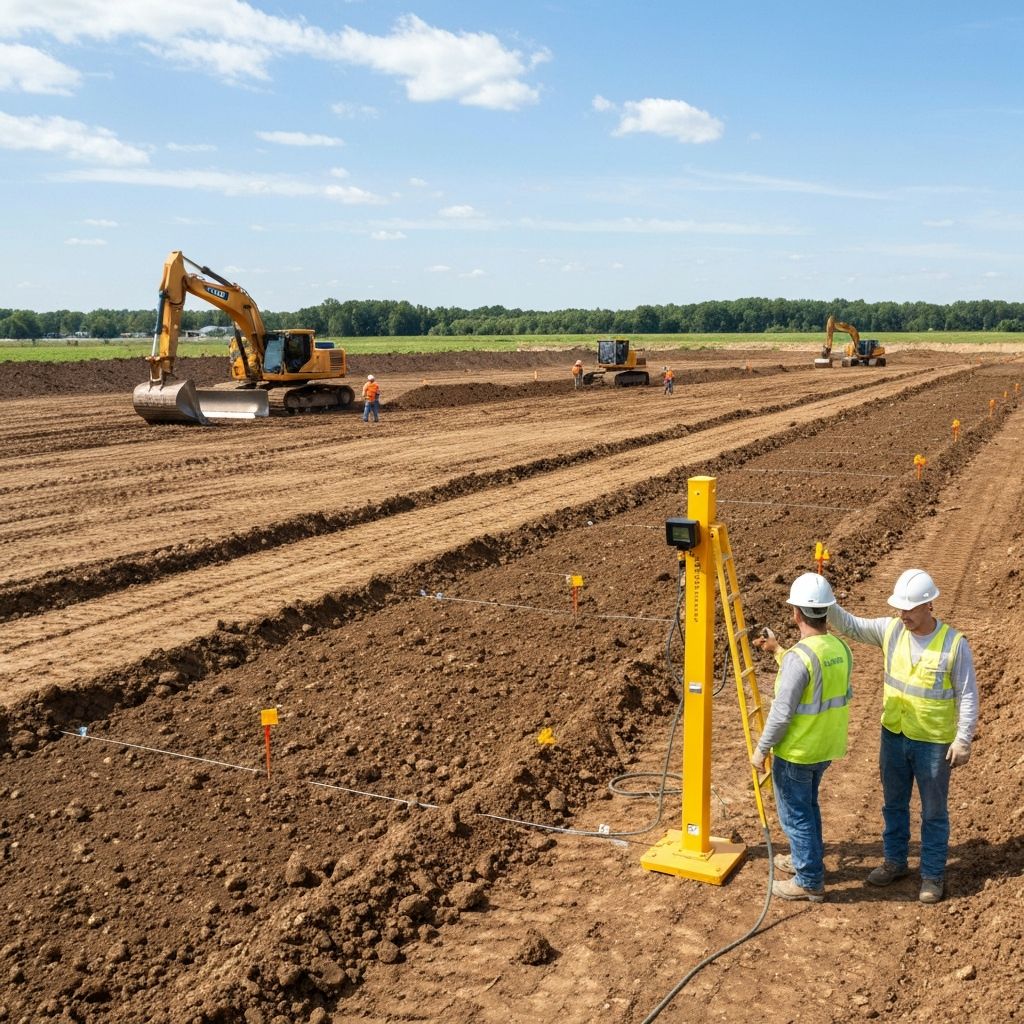
Soil compaction testing verifies that earthwork has been properly compacted to achieve the required density and bearing capacity. Adequate compaction is essential for foundations, roadways, embankments, and backfill to prevent settlement and structural distress. Field density testing compares in-place density to laboratory maximum density determined by Proctor tests, with acceptance typically 95-100% of maximum dry density depending on application.
Why Compaction Matters
Proper compaction increases soil strength, reduces settlement, decreases permeability, and improves load-bearing capacity. Under-compacted soil leads to foundation settlement, pavement failures, utility line breaks, and structural damage. Over-compaction can crush aggregates or create overly stiff layers that cause differential settlement. Consistent, verified compaction throughout construction is critical for long-term performance.
Field Testing Methods
Three primary methods are used for field density testing:
- Nuclear Density Gauge (ASTM D6938): Fast, non-destructive using gamma radiation to measure density and moisture content in 2-3 minutes
- Sand Cone Method (ASTM D1556): Traditional method using calibrated sand to measure excavated volume, accurate but time-consuming
- Drive Cylinder (ASTM D2937): Direct density measurement from extracted sample, good for fine-grained soils
- Lightweight Deflectometer (LWD): Measures stiffness/modulus rather than density, increasingly used in Europe
Testing Procedures and Frequency
Testing is performed at specified lift thicknesses (typically 150-300mm compacted thickness) before placing the next lift. Test locations are selected randomly or in a grid pattern at specified intervals (e.g., one test per 250m² or 500m³). Results are recorded with location coordinates, depth, moisture content, and percent compaction. Failed tests require reworking and retesting of the area.
Acceptance Criteria by Application
Structural fill under buildings: 95-98% of maximum dry density. Roadway subgrade: 95-100% depending on traffic class. Pavement base course: 98-100%. Utility trench backfill: 90-95% with restrictions on lift thickness. Behind retaining walls: 95% minimum to prevent lateral pressure from settlement. Specifications also limit moisture content to within ±2% of optimum moisture content.
Conclusion
Field density testing provides essential quality control for all earthwork operations. Our technicians perform compaction testing using nuclear gauges and sand cone methods with fast turnaround reporting. Contact us for geotechnical testing services.
Related Testing Services
- Proctor Compaction Test
- California Bearing Ratio (CBR)
- Plate Load Test
- Moisture Content Testing
Applicable Standards
Need This Testing Service?
Our accredited laboratories and field teams provide comprehensive testing services across Europe.
Contact Our Team